Cast parts are essential to modern manufacturing because they allow for the creation of complex and strong metal components at a low cost. Cast parts have been used in multiple industries, from automotive engines to machinery. This is due to the design flexibility, efficiency of materials, and scalability.
The guide will explain what castings are, their manufacturing process, the materials they’re made of, and the best way to select the right solution for you.
What are Cast Parts?
Castings are formed by pouring molten metal into a mould, then allowing the metal to cool down and solidify. The mold is then removed to reveal a part that has been finished or nearly completed. Further processing, such as heat treatment or machining, can be done.
Cast parts, unlike machined components, can have intricate geometries or internal cavities that would be otherwise difficult to manufacture.
Cast parts are commonly known by the following terms:
- metal castings
- Molded metal components
- Cast parts for industrial use
The types of casting processes used for cast parts
Different casting processes depend on the part complexity, selection of material, tolerances, and volume.
Sand Casting
Sand casting is a widely-used method for manufacturing cast parts. Sand-based moulds are used, which can be economical for larger or more complex parts.
Advantages:
- Tooling costs are low
- Large cast parts are suitable for this product.
- Material compatibility
Die Casting
Injection of molten steel into a mold is done under pressure. It is ideal for large-scale production that requires a high level of surface finish.
Most commonly used on aluminum and zinc parts.
Investment Casting
Investment casting, also known as lost wax process or smooth-surfaced investment casting, is a high-precision and surface finish method.
Perfect for:
- Geometries complexes
- Tolerances are tight
- Aerospace components and medical devices
Permanent Mold Casting
Sand casting is replaced by permanent mold casting, which uses metal molds that can be reused. This improves consistency and mechanical properties.
Centrifugal Casting
The centrifugal cast produces dense, defect-free cylindrical parts like pipes and rings by using rotational forces to evenly distribute the molten metal.
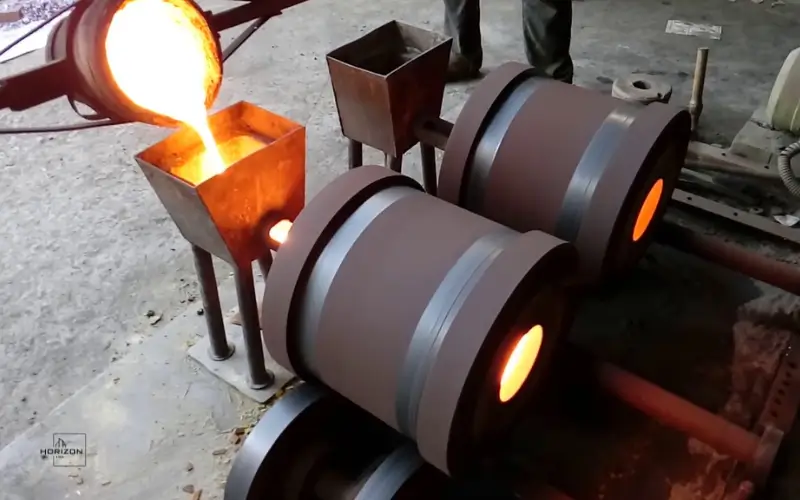


Material Commonly Used in Casting Parts.
The choice of material directly impacts the durability and performance, as well as cost.
Cast iron
Cast iron has excellent compressive strength, wear resistance, and vibration damping. Cast iron is used in engine blocks, machine frames, pipes, and other parts.
Aluminum Cast Parts
Aluminium casting is lightweight, resistant to corrosion, and has good thermal conductivity. Cast parts for automotive and aerospace are commonly used.
Steel Castings
Cast steel parts are strong and resistant to impact, so they can be used for a wide range of heavy-duty applications.
Castings in Brass and Bronze
Alloys based on copper are valued for their corrosion resistance, conductivity, and beauty.
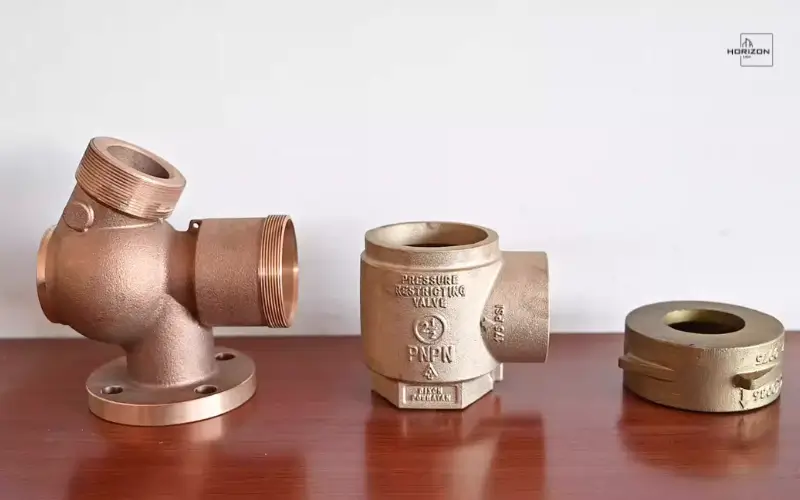


Common Types of Industrial Cast Parts
Cast parts are employed for a variety of industrial uses that include:
- Blocks for engines
- Housings for pumps
- Valve bodies
- Gear housings
- Manifolds
They are typically made in custom-cast pieces to satisfy certain operational requirements as well as dimensional specifications.
Industries That Use Cast Parts
Automotive Industry
Cast components are crucial in automobile manufacturing, such as transmissions, engines, suspension systems, and brake parts.
Aerospace Industry
Precision cast components are employed in housings, structural components, as well as heat-resistant pieces in aerospace and space-related applications.
Construction Industry
Structural castings and fittings, as well as heavy-duty support, are extensively utilized in both infrastructure and construction projects.
Oil and Gas Industry
The industry of oil and gas is dependent on casting parts including valves, flanges, as well as pressure housings, made to withstand the harsh conditions.
Industrial Machinery
Heavy machinery utilizes sturdy cast components for frames, gears, as well as enclosures, which require long-lasting service and dependability.


Advantages of Using Cast Parts in Manufacturing
The advantages of casting parts are numerous when compared to other manufacturing techniques:
- Capability to design complicated forms
- Cost-effective for large production volumes
- Effective use of materials
- The need for extensive machining is reduced.
- Fantastic mechanical properties
In comparison to forging or machined components,sCast parts usually offer an even mix of toughness, flexibility, ty, and cost.
Quality Standards and Tolerances for Cast Parts
The quality control aspect is crucial when casting. Trustworthy manufacturers use internationally recognized norms, such as those of ASTM International, ISO, and SAE International.
The most important quality aspects comprise:
- Dimensional tolerances
- Surface Finish
- Testing of mechanical components
- Non-destructive Inspection
Post-Casting Processes for Cast Parts
Following casting, the parts can undergo further processes in order to improve efficiency and ensure accuracy.
- Treatment to increase durability
- Machining to high-quality tolerances
- Finishing the surface to resist corrosion
- Testing and quality inspection
This ensures that the casting parts are in compliance with the requirements of each application.
How to Choose the Right Cast Parts Manufacturer
The selection of the best company is vital to maintain high-quality and reliability. Take into consideration the following aspects:
- The capabilities of casting and foundry processes, as well as casting methods.
- The material expertise
- Prototyping and custom design support
- Systems for quality assurance
- Lead times and production scalability
Custom Cast Parts Solutions by Horizon
On horizon.com, we provide efficient and premium cast parts that can be designed to meet the needs of your specific industry. From the selection of materials to the closing inspections, customized casting solutions provide longevity, accuracy, and efficiency across many uses.