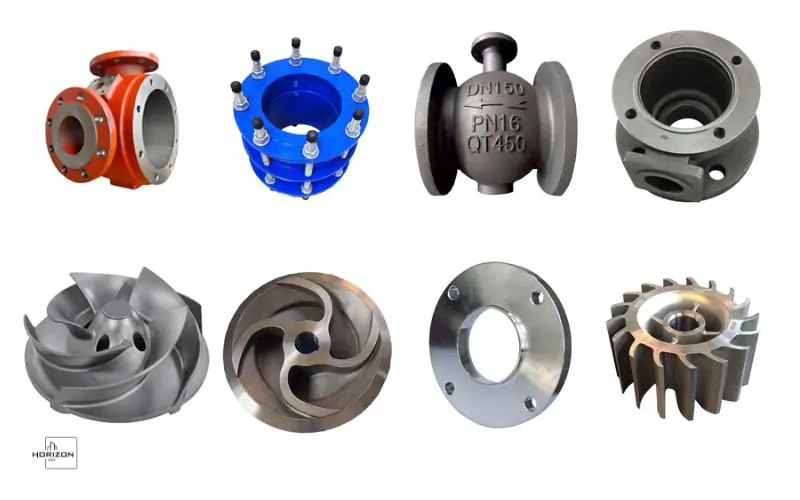
Casting spare parts is the basis of automobiles, industrial systems, construction equipment, and other heavy engineering systems. They are made with advanced processes for metal casting, which allow the manufacturers to make robust, high-strength components with intricate geometric shapes. From valve housings for engines and engine bodies, to pumps and gear, casting spare parts guarantee durability and long-term reliability.
This comprehensive manual, we look at the basic principles, casting spare parts manufacturing procedures involved choosing the material used, Industrial applications, the importance of quality, and top methods. Its goal is to give the reader a comprehensive understanding of the subject, with a professional, clear, and authoritative style.
Understanding Casting Spare Parts in Industrial Manufacturing


Casting spare parts are parts made by pouring molten metal into a mold. It then solidifies to form a particular form. After cooling, the molded part is taken out, polished, and, if needed made machined to meet exact tolerances. This process allows an efficient manufacturing process for parts that are otherwise hard or expensive to manufacture with traditional techniques of machining.
The widespread usage of casting spare part in industries is fueled by their solidity, as well as design flexibility and efficiency in cost. Casting allows manufacturers to make extremely complex and simple parts while maintaining a standard of quality.
Why Casting Is a Preferred Method for Spare Parts Production
Casting is one of the most reliable techniques of manufacture for spare components due to the capacity to mix the strength of a cast part with its versatility, as well as scalability. In contrast to machines or manufactured components, casting parts are able to be manufactured in huge quantities while preserving the uniform properties of the material throughout the entire structure.
Another benefit of casting spare parts lies in their ability to be adapted to various materials and alloys. The flexibility of casting spare parts allows manufacturers to pick materials that meet the mechanical specifications, like the strength as tensile or wear resistance, thermal stability, and corrosion resistance.
Overview of Casting Processes Used for Spare Parts

The casting process used is different according to the complexity of the design and material specifications, as well as the production capacity, and the final use of the spare component.
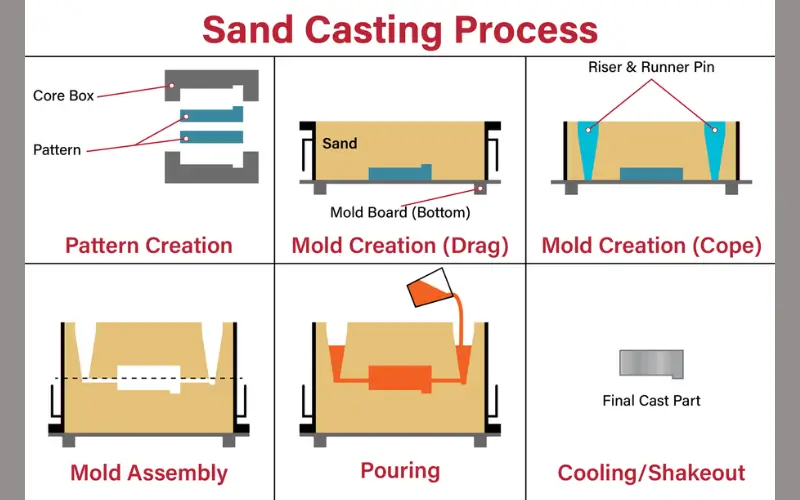
Sand Casting for Heavy and Industrial Components
Sand casting is among the most commonly used techniques in the production of casting spare parts, specifically for huge and heavy parts. The molds are made by mixing sand with which makes it ideal to produce parts that have large dimensions as well as thick segments. Sand casting is typically utilized for making manufacturing housings for industrial engines, pumps, casings for pumping, and other structural machines.
Die Casting for Precision and High-Volume Production
Die casting can be described as a pressure casting method that is mostly used for non-ferrous metals like zinc and aluminum. This process is great for making spare parts that need precise dimensional precision and smooth surfaces, as well as tight tolerances. Die casting spare components are commonly utilized in the auto production line, consumer electronics, as well as electronic enclosures.
Investment Casting for Complex and High-Accuracy Parts
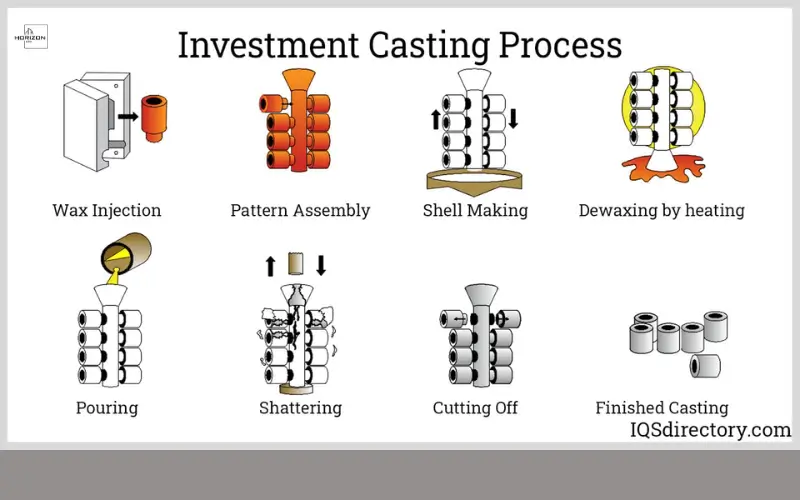

The investment casting process, which is also referred by the name of lost wax casting, is used when extreme accuracy and precise particulars are required. It allows companies to make near-net-shape parts that require minimal post-machining. Parts made of investment casting can be found for aerospace equipment, medical devices, and industrial machinery.
Centrifugal and Permanent Mold Casting Applications
The centrifugal casting process is utilized for parts that are cylindrical or rotational, where the density of the material and its uniformity are crucial. Permanent mold casting, however, is suited for medium-volume production and provides superior mechanical properties over the sand casting method. Both techniques are employed in hydraulic systems, mechanical assemblies, bearings, and other components.
Materials Commonly Used in Casting Spare Parts
Selection of the right material plays an essential role in determining performance as well as the durability, application, and the casting parts are suitable for.
Ferrous Materials in Casting
Cast iron is among the most widely used components because of its superior performance in reducing wear, vibration, as well as its cost-effectiveness. Ductile iron provides enhanced tensile strength and resistance, which makes it ideal for use in heavy-duty and automotive components. Carbon steel as well as alloy steel castings are employed to increase the strength of structural components, as well as load-bearing capacities are needed.
Non-Ferrous Materials in Casting
Aluminum casting is favored in situations where weight reduction as well as corrosion resistance are important, specifically in the aerospace and automotive industries. Bronze and brass castings are admired because of their strength as well as resistance to corrosion. They are ideal for fittings, valves, as well as bearing components. Zinc alloys are commonly utilized in die castings for high-precision spare parts with intricate forms.
Industrial Applications of Casting Spare Parts
Casting spare parts are utilized widely across a range of industries because of their flexibility as well as their mechanical toughness.
Automotive and Transportation Sector
Within the automotive sector, casting spare components can be found in engine systems and braking assemblies. They also serve as transmission housings, as well as suspension elements. The parts have to be resistant to high temperatures, mechanical strain, and constant operation.
Manufacturing and Industrial Equipment
Production plants depend on casting spare parts to build frames for machinery, as well as pump housings, gear housings, conveyors, and compressors. Cast components’ durability guarantees reliable performance in harsh industrial settings.
Oil, Gas, and Power Generation
Casting spare components plays a vital part in the extraction of oil and gas, along with power plants s as well as energy infrastructure. Valve bodies, flanges, turbine housings, and components that resist pressure are made with high-quality casting material.
Construction, Mining, and Agriculture
The heavy equipment that is used in mining, construction, as well applications relies heavily on casting spare parts that can withstand extreme loads and extreme operating conditions. They are engineered for extended service lives and low maintenance.
Quality Control and Standards in Casting Spare Parts Manufacturing
Consistent quality is a must for casting spare parts production. Control processes for quality are in place throughout the manufacturing process, beginning with the choice of raw material through the final inspection. Material composition, dimensional accuracy, as well as surface integrity are monitored closely to ensure conformity with the industry standards.
International standards like ISO, ASTM, DIN, and ANSI offer guidelines on materials’ properties, testing methods, as well as quality control methods. Following these standards guarantees security, compatibility, and the performance of products across different markets.
Machining, Heat Treatment, and Finishing Processes
Even though casting creates near-perfect designs, additional processes are typically required to obtain precision tolerances and specific performance. CNC-machined parts are commonly employed to fine-tune critical dimensions as well as heat treatment to increase the strength, hardness, and resistance to wear.
Techniques for finishing the surface, like polishing, coating, and painting, can improve the resistance to corrosion and aesthetic value. This process ensures that the casting parts are in compliance with the requirements of both visual and functional aspects.
OEM and Aftermarket Casting Spare Parts
Casting spares are made by both the original equipment manufacturer as well as aftermarket market replacements. OEM parts are made following the original specifications of design and are designed for use on new equipment. Parts for casting that are available aftermarket provide affordable solutions for repair and maintenance, while ensuring the acceptable standards of performance.
Global Sourcing of Casting Spare Parts
Global sourcing is now an approach for businesses that want to cut costs while also having access to specialist foundries. Numerous manufacturers procure casting spare parts from areas that have strong casting capabilities and modern production capabilities. Successful sourcing requires supplier assessment, quality audits, and coordination of supply chains to guarantee consistency in outcomes.
Future Developments in Casting Spare Parts Manufacturing
Innovations in software for simulation technology, automation, as well as digital manufacturing are changing the world of casting. Modern foundries are using advanced technologies that improve processes, minimize errors, and increase the ability to trace. Initiatives for sustainability, like recycled metals and energy-efficient production techniques, are shaping how casting part production is done.
Conclusion
Casting spares are an integral part of the production and maintenance of equipment in the industrial sector. Their capacity to offer the strength, durability, and design flexibility makes they indispensable in a vast spectrum of sectors. With a thorough understanding of casting processes and materials, as well as high-quality standards and techniques for sourcing, businesses are able to make educated decisions that will ensure the longevity of their operation.
Must visit:
Product Sourcing Solution
Product Development Logistics and Supply Chain Solutions for Product Brands